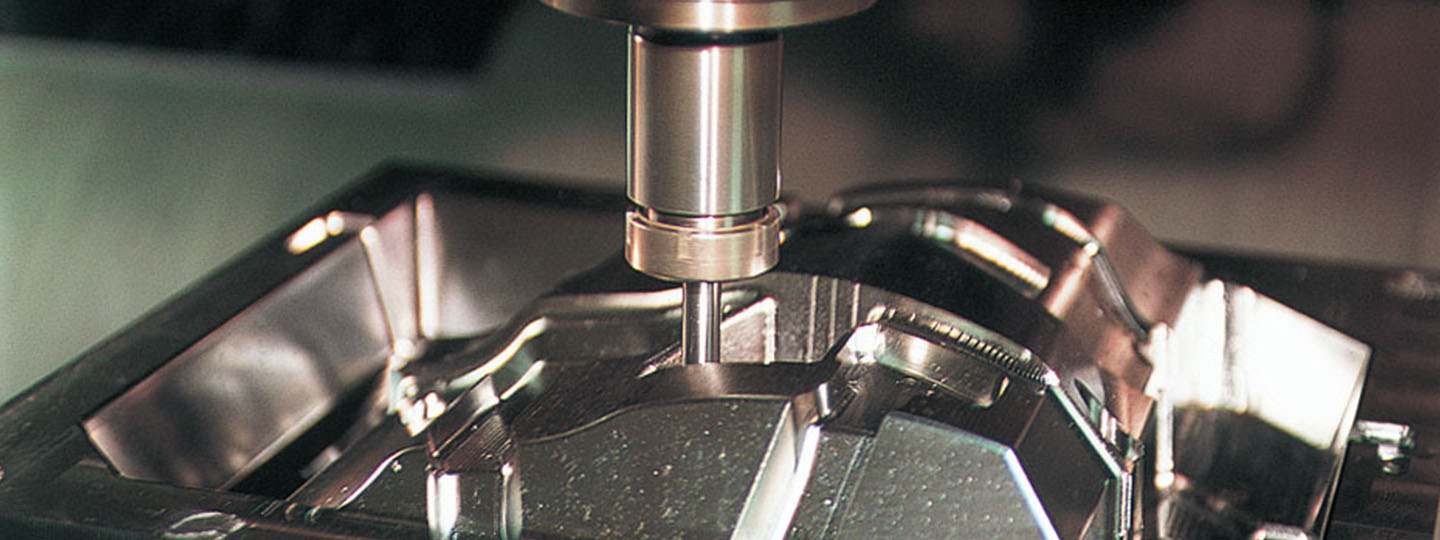
Ryobi produces top-quality die cast products by integrating the technical capabilities cultivated over many years.
The Ryobi Group's Casting Technologies
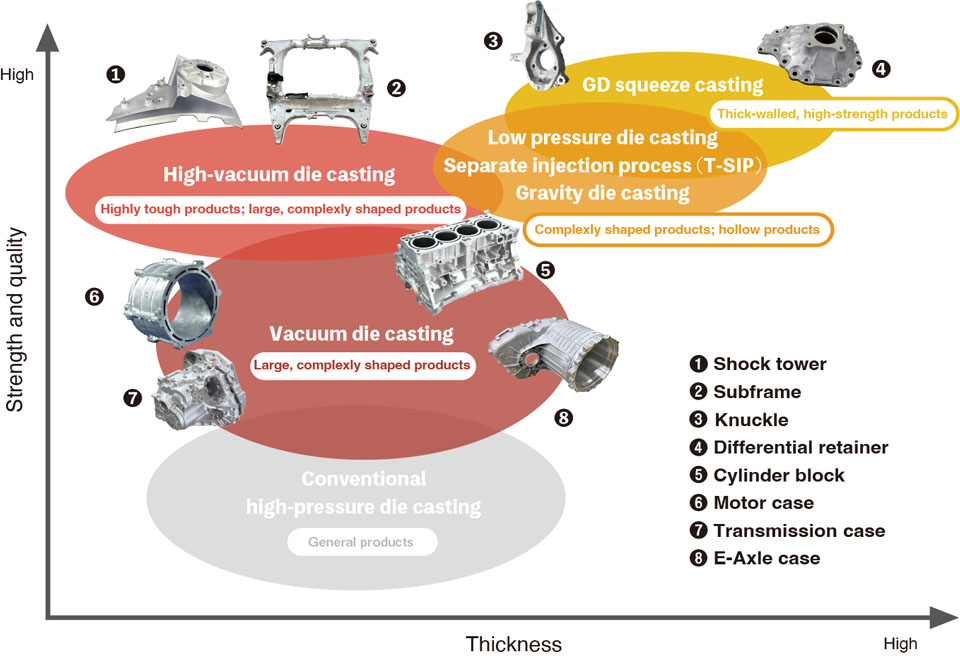
The Ryobi Group manufactures top-quality products using production methods best suited to individual customer's needs.
High-Vacuum Die Casting Technology
In die casting, when molten metal (molten aluminum alloy, etc.) is fed into a die at high speed under high pressure, air and gas can get trapped in the molten metal, resulting in such internal defects as blow holes in the cast item. These residual gases trapped inside the castings cause to get blisters on the castings after high-temperature heat treatment and welding. Therefore, it is difficult to manufacture parts that require heat treatment and welding, such as body and chassis parts, by using conventional high-pressure die casting.
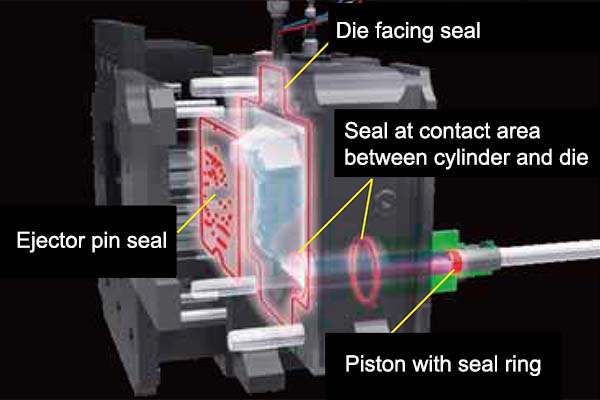
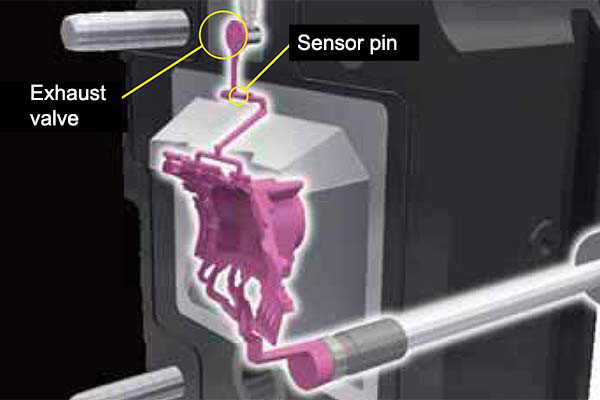
In Ryobi's high-vacuum die casting, a large-capacity vacuum system is used to remove the air to ensure this process is carried out in a near vacuum, with the molten metal fed into a die that has been completely sealed to ensure airtightness. Ryobi's original vacuum device (RSV, new RSV) mounted inside the die has a sensor that monitors the molten metal as it fills the mold and closes the valve at the appropriate time to prevent molten metal from entering the vacuum's path.
The products of high-vacuum die casting can be heat-treated and welded and can be used in automobile body and chassis parts that require high mechanical properties, which is simply not possible with conventional die cast products. The high internal quality and high ductility of the castings, which resist impact fractures, enable them to be used in parts critical to vehicle safety like subframes that support suspension and assist in body rigidity.
GD Squeeze Casting
GD squeeze casting is a new casting method unique to Ryobi that combines gravity die casting and the squeeze casting method. This method is suitable for manufacturing relatively thick-walled products with high strength and quality requirements, which is difficult to achieve with other casting methods.
As the die is filled with molten metal (molten aluminum alloy, etc.) via gravity, it is held in a tilted position. The slow filling of the die prevents air from being entrapped in the molten metal. This is called laminar flow filling. Solidification of the molten metal causes shrinkage as it cools, but that shrinkage is reduced by pressure from squeeze pins. This prevents the occurrence of internal defects called shrinkage cavities.
GD squeeze casting prevents air entrapment by laminar flow filling, the main feature of gravity die casting, enabling heat treatment and welding after forming. In addition, pressurization, a feature of the high-pressure solidification casting method (pressure from squeeze pins), reduces variations in quality. These features enable us to manufacture top-quality, high-strength, high-ductility products suitable for automotive suspension parts.

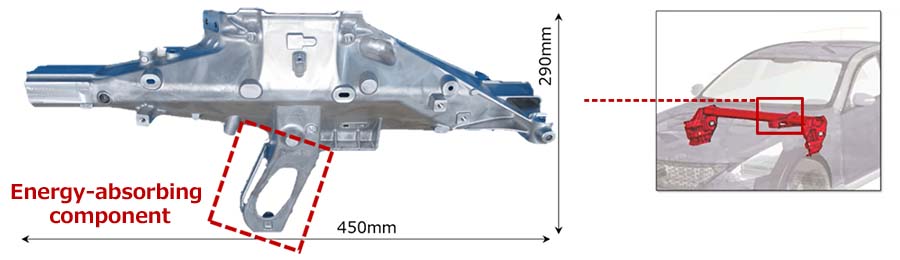
Producing an Energy-Absorbing Steering System Support Component Using Integrated Molding
Ryobi aims to further expand the applications of die casting and, to this end, undertakes the development of innovative technologies and new manufacturing methods. A prime example of its efforts is a proprietary die casting technology used for the integrated molding of an energy-absorbing support component for a steering system. Having developed this technology, Ryobi was chosen to receive the Sokeizai Industry Technology Award and is otherwise regarded highly for its technological capabilities.
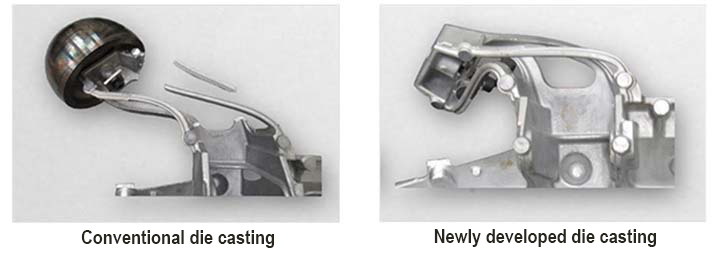
Steering system support components are designed to reduce vibrations felt through the steering wheel and play an essential role in ensuring driver safety. While the support components of steering systems generally consist of multiple steel press parts, Ryobi has developed a die casting technology to manufacture this component using aluminum, which is lighter than steel, as raw material. Aluminum die casting not only helps create lightweight parts but also grants greater freedom in determining the shapes of the resulting products, while allowing for the efficient placement of ribs* on component surfaces. Taking full advantage of these features, we created a steering system support component boasting greater stiffness without increasing weight. Moreover, although the die casting of such energy-absorbing components of steering system supports has long been considered difficult due to the high ductility required of this component, we developed new materials as well as technologies that enabled us to enhance the quality of die casting, thereby meeting this requirement. At the same time, we realized an integrated molding technology that made the manufacture of this component possible. With regard to performance during collisions, this component deforms and absorbs energy, preventing the steering shaft from intruding into the passenger compartment.
* Structural bracing perpendicular to plane surfaces that reinforces flat or thin sections
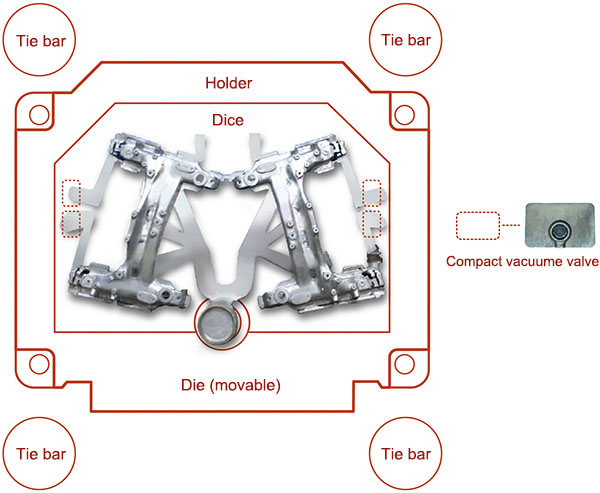
Two-Cavity Die for Large Die-Cast Products
To control new investment and increase manufacturing efficiency in the mass production of large die cast products, Ryobi has developed top-quality large, two-cavity die casting technology. The optimization of die design through CAE simulation, including the efficient placement of runners, and our original compact vacuum device (new RSV) have made it possible to downsize the die. In general, two-cavity casting requires low-pressure molten metal filling due to the large projected area of the product, but Ryobi has applied high-vacuum die casting technology to two-cavity casting, enabling top-quality products.